What are Static Frequency Converters (SFC)?

A static frequency converter is an advanced electronic device that transforms electrical power from one frequency to another without using any moving parts. Unlike traditional rotary converters, these modern power conversion systems use sophisticated semiconductor technology to provide clean, reliable frequency conversion for various industrial and commercial applications.
Static frequency converters work by first converting incoming AC power to DC, then regenerating it back to AC at the desired output frequency. This process ensures precise control over voltage, frequency, and power quality, making them essential equipment for industries requiring specific electrical standards.
PEOPLE ALSO READ : Best SoundCloud to MP3 Converter [2025]
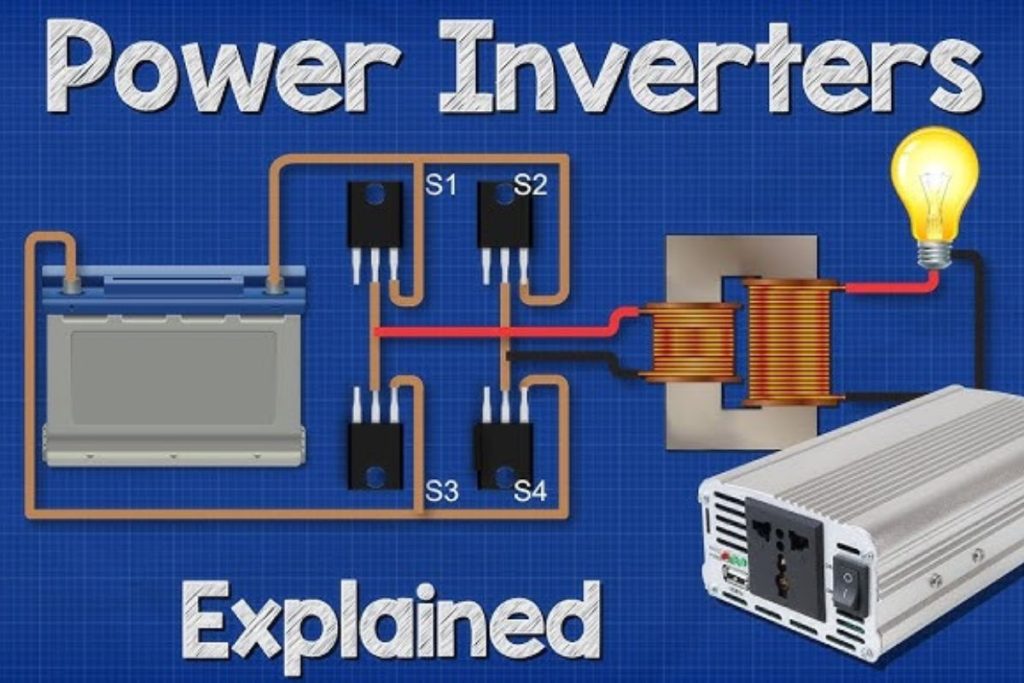
How Static Frequency Converters Work
The operation of static frequency converters involves three main stages:
- Rectification Stage: Converts incoming AC power to DC using advanced IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) technology
- DC Link Stage: Smooths and filters the DC power using capacitors and inductors
- Inversion Stage: Regenerates clean AC power at the required output frequency using PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) control
This process allows for precise control over output parameters, including voltage regulation, frequency stability, and harmonic distortion reduction.
Types of Frequency Converters
Static Frequency Converters vs Rotary Frequency Converters
Understanding the difference between static and rotary frequency converters enables informed decisions for your power conversion needs.
| Feature | Static Frequency Converter | Rotary Frequency Converter |
| Size & Weight | Compact and lightweight | Large and heavy |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance (no moving parts) | High maintenance (mechanical parts) |
| Efficiency | 85-95% efficiency | 70-85% efficiency |
| Noise Level | Silent operation | Noisy due to mechanical parts |
| Initial Cost | Lower upfront investment | Higher initial cost |
| Installation | Simple wall or floor mounting | Requires reinforced flooring |
| Reliability | High reliability | Moderate reliability |
Static frequency converters are smaller, lighter, and almost always more affordable than their rotary counterparts. This makes them ideal for applications where space and budget constraints are important factors.
Frequency Converter Categories by Output
Modern static frequency converters can produce various output frequencies to meet different application requirements:
- 400Hz Converters: Primarily used in aviation and aerospace applications
- 100Hz Converters: Common in specialized industrial equipment
- 60Hz Converters: Standard for North American equipment
- 50Hz Converters: Standard for European and Asian equipment
- 25Hz Converters: Used in railway traction systems
Benefits and Advantages of Static Frequency Converters
Key Benefits
Static frequency converters provide efficient, noise-free, and highly reliable frequency conversion, allowing seamless operation of equipment that requires a different frequency from the main power supply.
Energy Efficiency: The converter enhances power usage efficiency and reduces energy consumption, resulting in much lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Reliability: Static frequency converters provide a stable power supply, which is critical for sensitive equipment.
Flexibility: Variable output capabilities allow customized frequency settings for specific applications.
Cost-effectiveness and Performance
Static converters generally use less energy than their rotary counterparts, which can result in significant cost savings over time. The absence of moving parts also reduces maintenance costs and increases overall system reliability.
PEOPLE ALSO READ : Protocol Converter Basics Everything You Need to Know
Applications and Industries
Where Static Frequency Converters are Applied
SFCs find many applications because of frequency conversion needs: powering equipment for different electrical standards, supporting renewable energy systems, and powering special industrial machinery.
Rail Applications
Railway systems worldwide use different traction frequencies. Static frequency converters enable:
- Seamless integration between different railway networks
- Efficient power transfer from utility grids to railway systems
- Reduced energy losses in traction applications
Marine Applications
Shore-to-ship power systems require frequency conversion to:
- Reduce emissions while ships are docked
- Provide stable power for ship operations
- Meet international maritime electrical standards
Industrial Applications
Connecting industrial, utility, and rail applications to the electrical supply with differing voltage and frequency is a complex task that static frequency converters solve efficiently.
Industries That Need Frequency Converters
Power Generation: Grid interconnection between systems with different frequencies
Aviation: Ground support equipment requiring a 400Hz power supply
Manufacturing: International equipment integration and testing facilities
Testing Laboratories: Precise frequency control for equipment certification
Technical Specifications and Features
Key Technical Parameters
Modern static frequency converters offer:
- Input Voltage Range: 380V-480V (3-phase)
- Output Frequency: Variable (typically 25Hz-400Hz)
- Efficiency: Up to 95%
- Power Factor: >0.95
- Harmonic Distortion: <3% THD
- Response Time: <50ms
A static frequency converter utilizing digital signal processing technology can provide precise data for voltage, frequency, current, power factor, and other parameters.
Advanced Control Features
- DSP-based digital control systems
- Real-time monitoring and diagnostics
- Remote control and monitoring capabilities
- Automatic fault detection and protection
- Programmable output parameters
Selection and Implementation Guide
Choosing the Right Static Frequency Converter
When selecting a static frequency converter, consider:
- Power Rating: Match converter capacity to load requirements
- Input/Output Specifications: Ensure compatibility with existing systems
- Environmental Conditions: Temperature, humidity, and altitude requirements
- Application Type: Continuous duty vs intermittent operation
- Future Expansion: Consider scalability needs
Installation Considerations
- Space Requirements: Compact design allows flexible installation
- Cooling Requirements: Adequate ventilation for optimal performance
- Electrical Connections: Proper grounding and protection systems
- Environmental Protection: IP rating suitable for installation environment
PEOPLE ALSO READ : Industrial Media Converter Guide 2025
Conclusion
Static frequency converters represent the future of power conversion technology, offering superior efficiency, reliability, and flexibility compared to traditional rotary systems. Frequency converters are valuable tools that enable individuals or industries to take AC energy from one region, transform it into DC power, and safely convert it back to AC with a different frequency.
Whether you need frequency conversion for industrial equipment, railway systems, marine applications, or testing facilities, static frequency converters provide the precision and reliability required for mission-critical operations. Their compact design, low maintenance requirements, and high efficiency make them the preferred choice for modern power conversion applications.
By understanding the benefits, applications, and technical specifications outlined in this guide, you can make informed decisions about implementing static frequency converter technology in your operations. The investment in quality static frequency conversion equipment pays dividends through improved efficiency, reduced maintenance costs, and enhanced operational reliability.
READ MORE : Super Converters

